In Internet networking, a private network is a computer network that uses a private address space of IP addresses. These addresses are commonly used for local area networks (LANs) in residential, office, and enterprise environments. - Wikipedia
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) has reserved the following three blocks of the IP address space for private internets:
10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255 (10/8 prefix)
172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255 (172.16/12 prefix)
192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 (192.168/16 prefix)
Internet Service Provider
My consulting business utilises a small business NBN plan (100/40 Mbps) and the provider supplied a Gateway (a modem-router combination) with support for FTTN.
The Gateway address is 192.168.20.1
Subnets
I want to divide my network into two or more subnets.
For example, devices connected to my ISP's Gateway will be allocated addresses in the range 192.168.20.2 - 192.168.20.254. Devices connected to my Synology NAS's eth1 port will be allocated addresses in the range 192.168.21.2 - 192.168.21.254.
ISP Gateway (192.168.20.1) -> Synology NAS eth0 (192.168.20.2)
Synology NAS eth1 (192.168.21.1) -> Netgear Switch (192.168.21.2) -> RPi
ISP Gateway - Static IP Lease
I used the Gateway's web UI (Advanced -> Local Network -> LAN) to configure a static IP lease for the NAS (eth0):
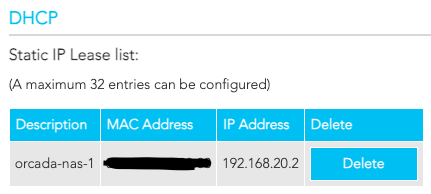
You can use the following command to obtain a MAC address:
ethtool -P eth0
Synology DiskStation Manager (DSM) - Static IP
I used the Synology DiskStation Manager (DSM) to configure static IP's for the NAS's ethernet interfaces:
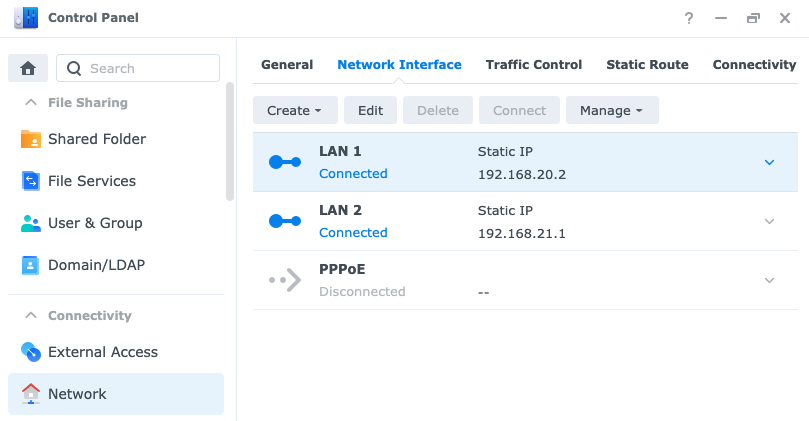
Synology DiskStation Manager (DSM) - DHCP Server
I used the Synology DiskStation Manager (DSM) to configure the NAS's DHCP Server:
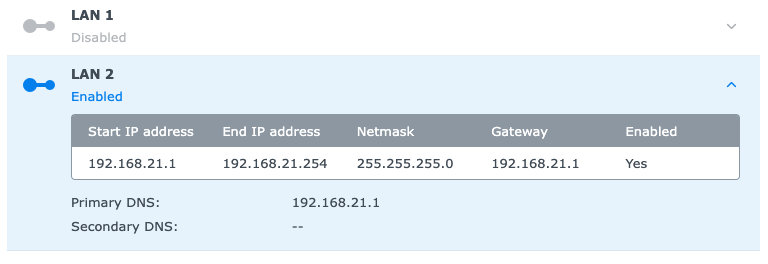
I also used the NAS's DHCP Server to configure a static IP lease for my Netgear switch (192.168.21.2).
I used the Netgear switch's web UI to configure a static IP (192.168.21.2):
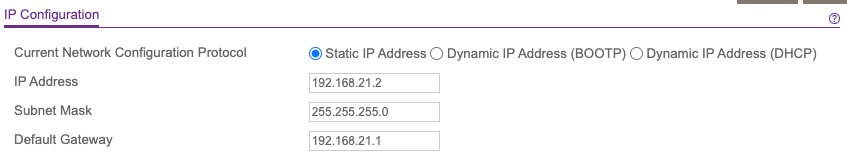
ISP Gateway - Static Routes
I used the Gateway's web UI (Advanced -> Routing) to configure a static route to the subnet (192.168.21.0/24):
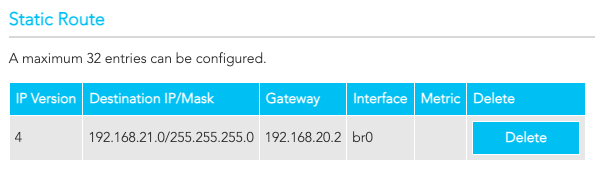
Note: The static route 'Gateway' setting is for the next hop (i.e., if the gateway's IP address is: 192.168.20.1 the next hop is 192.168.20.2).
Ping a device in the subnet
If you can't ping a device in the subnet you may need to use the sysctl command to enable IP forwarding (on the NAS).
sudo sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
To make the change persistent, you need to edit the /etc/sysctl.conf file:
sudo nano /etc/sysctl.conf
And add the following line to the bottom of the file:
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
References
- Raspberry Pi Stack Exchange: How do I set up networking/WiFi/Static IP
- Linux.com: Linux Routing Subnets Tips and Tricks
- dd-wrt.com Wiki: Linking Subnets With Static Routes
