In a previous post, I wrote about setting up my Raspberry Pi 3 PicoCluster.
In this post, I'll walk you through the steps I followed when setting up Docker Swarm Mode on my Raspberry Pi 3 PicoCluster.
Install Docker
We can download the latest .deb package (for the RPi 3's ARM architecture) from Docker's packagecloud.io repo:
wget https://apt.dockerproject.org/repo/pool/main/d/docker-engine/docker-engine_1.12.3-0~jessie_armhf.deb
And, copy (scp) it to each node:
export FILE=docker-engine_1.12.3-0~jessie_armhf.deb
export USER=picocluster
scp $FILE $USER@pc0:$FILE
scp $FILE $USER@pc1:$FILE
scp $FILE $USER@pc2:$FILE
scp $FILE $USER@pc3:$FILE
scp $FILE $USER@pc4:$FILE
Now, we can install Docker and add the "picocluster" user to the Docker group (repeat for each node):
ssh manager sudo apt install libapparmor1
ssh manager sudo dpkg -i $FILE
ssh manager sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
Note: In a previous post, I setup a SSH configuration file to save key strokes and to make things much easier to remember.
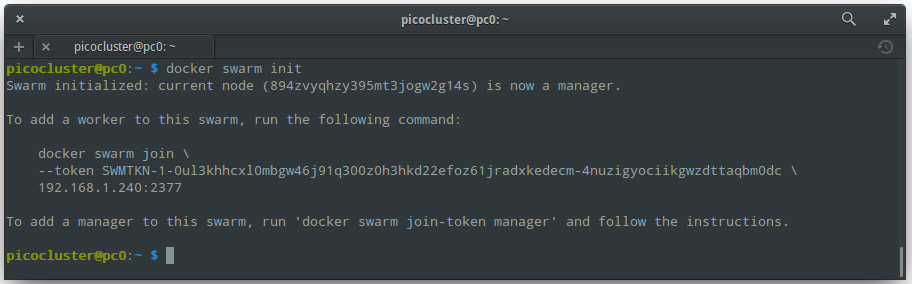
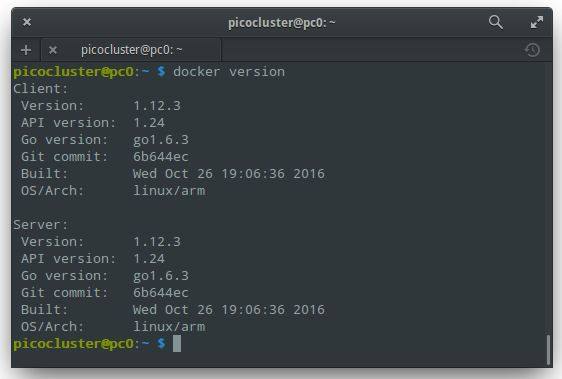
Check that everything is OK:
ssh manager
docker version
You should see output like:
Create a swarm
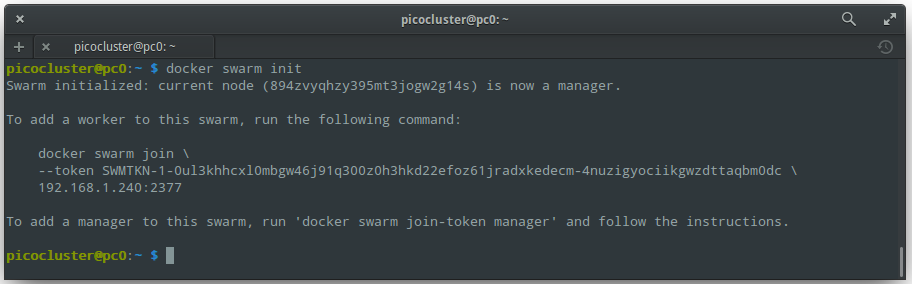
Now, we can bootstrap the manager node:
docker swarm init
You should see output like:
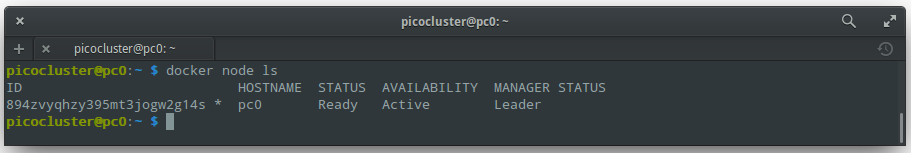
Check that everything is OK:
docker node ls
You should see output like:
To join the swarm as a worker we first need to retreive the join token for worker nodes (from the manager node):
docker swarm join-token --quiet worker
You should see output like:
SWMTKN-1-0ul3khhcxl0mbgw46j91q300z0h3hkd22efoz61jradxkedecm-4nuzigyociikgwzdttaqbm0dc
Now, we can bootstrap some worker nodes:
function getip() { (traceroute $1 2>&1 | head -n 1 | cut -d\( -f 2 | cut -d\) -f 1) }
export TOKEN=SWMTKN-1-0ul3khhcxl0mbgw46j91q300z0h3hkd22efoz61jradxkedecm-4nuzigyociikgwzdttaqbm0dc
export MANAGER_IP=$(getip pc0)
export PORT=2377
ssh worker-1 docker swarm join --token $TOKEN $MANAGER_IP:$PORT
ssh worker-2 docker swarm join --token $TOKEN $MANAGER_IP:$PORT
ssh worker-3 docker swarm join --token $TOKEN $MANAGER_IP:$PORT
ssh worker-4 docker swarm join --token $TOKEN $MANAGER_IP:$PORT
To view the current state of the swarm:
docker info
You should see output like:
Containers: 0
Running: 0
Paused: 0
Stopped: 0
Images: 0
Server Version: 1.12.3
...
Swarm: active
NodeID: 894zvyqhzy395mt3jogw2g14s
Is Manager: true
ClusterID: 5bxf4abzgdfbao2q70owqm4bh
Managers: 1
Nodes: 5
...
To view information about nodes:
docker node ls
You should see output like:
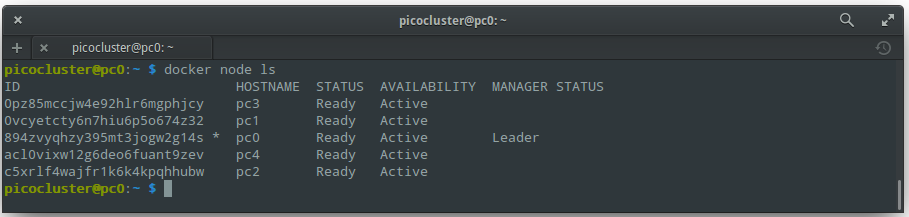
Deploy a service to the swarm
Now, lets bring up a container:
docker service create --replicas 1 --name ping hypriot/rpi-alpine-scratch ping docker.com
To see a list of running services:
docker service ls
You should see output like:
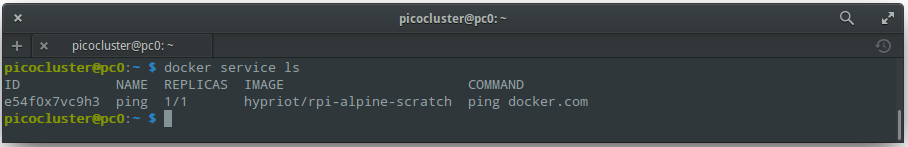
To scale up the number of tasks:
docker service scale ping=10
You should see output like:
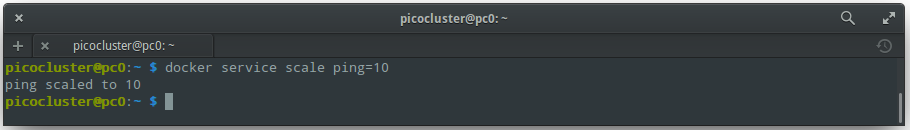
To list a service's tasks:
docker service ps ping
You should see output like:
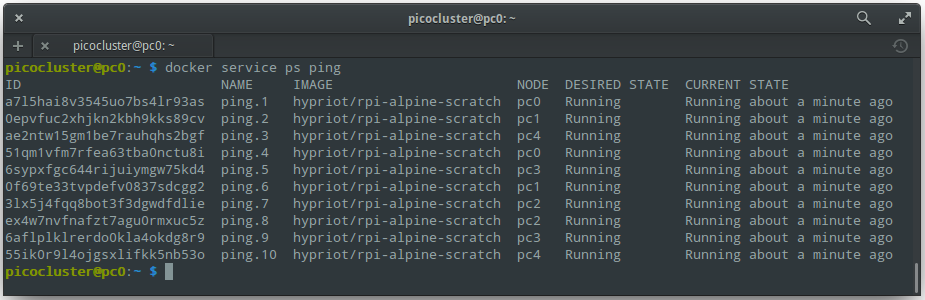
To remove the service:
docker service rm ping
Way cool :)
References:
- Docker Docs: Run docker-engine in Swarm Mode
- Docker Docs: Getting started with Swarm Mode
- Hypriot on Docker Hub: Raspberry Pi (ARM) Images
- The Raft Consensus Algorithm: What's odd about that?